What is the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase
The diabetes honeymoon phase, also known as the remission phase, is a period that sometimes occurs shortly after the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. During this phase, individuals may experience a temporary improvement in their blood sugar control, and they might require less insulin or, in some cases, even no insulin at all for a period of time. This can be a confusing time for those newly diagnosed, as it might seem like their diabetes is disappearing. However, it’s important to understand that the honeymoon phase is a natural part of the disease process and doesn’t indicate a cure.
Definition of Diabetes Honeymoon Phase
The honeymoon phase in diabetes is characterized by a temporary period where the body’s insulin needs decrease. This occurs because, after diagnosis, the remaining beta cells in the pancreas (the cells that produce insulin) may still be functioning to some degree. As a result, the body may require a lower dose of insulin injections or insulin pump therapy to maintain stable blood sugar levels. It is essentially a period of relative remission, but not a cure. The underlying autoimmune process that destroys the beta cells continues, meaning that eventually, the honeymoon phase will end.
Who Experiences the Honeymoon Phase

The honeymoon phase is most commonly observed in individuals newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. It’s less common in those with type 2 diabetes, although it can sometimes occur. The likelihood of experiencing the honeymoon phase varies, with some people going through it and others not. Factors such as age, the initial severity of the diabetes, and the treatment plan implemented after diagnosis can influence whether a person enters the honeymoon phase. It is important to note that not everyone newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes will experience this phase.
Duration of the Honeymoon Phase
The duration of the honeymoon phase can vary significantly from person to person. It might last for a few weeks, several months, or even up to a year or more. There is no way to predict precisely how long it will last for an individual. Eventually, the remaining beta cells will become unable to produce enough insulin, and the body’s insulin needs will gradually increase. This marks the end of the honeymoon phase, and the individual will typically require a higher insulin dosage to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Therefore, ongoing monitoring and adjustments in treatment are essential during and after the honeymoon phase.
Top 5 Things to Know About the Diabetes Honeymoon Phase
Understanding the diabetes honeymoon phase can help you better manage your diabetes and set realistic expectations. Here are five key things to keep in mind during this phase of your diabetes journey.
Insulin Dosage Adjustments

During the honeymoon phase, insulin needs may decrease. You might find that you require less insulin than initially prescribed, or you might temporarily need no insulin at all. It’s crucial to work closely with your healthcare team to adjust your insulin dosage based on your blood sugar readings. Never alter your insulin dosage without consulting your doctor. Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential to guide these adjustments. This is not a sign of a cure, but it presents an opportunity to optimize your insulin regimen and minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Frequent blood sugar monitoring is vital during the honeymoon phase. Check your blood glucose levels regularly, as advised by your healthcare provider. This helps you understand how your body is responding to insulin and other factors like diet and exercise. Keep a detailed log of your blood sugar readings, including the time of day, the amount of insulin administered, and any relevant details like meals or activity. This data provides valuable information for your healthcare team to make informed decisions about your treatment plan. Using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can also be particularly helpful during this time, providing real-time glucose readings.
Importance of Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise is even more critical during the honeymoon phase. A balanced diet, rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, which reduces the amount of insulin your body needs. Work with a registered dietitian or certified diabetes educator to create a meal plan tailored to your individual needs. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. These lifestyle choices will support your blood sugar management and overall health during and beyond the honeymoon phase. See image: Healthy diet diabetes.
Recognizing the End of the Honeymoon Phase
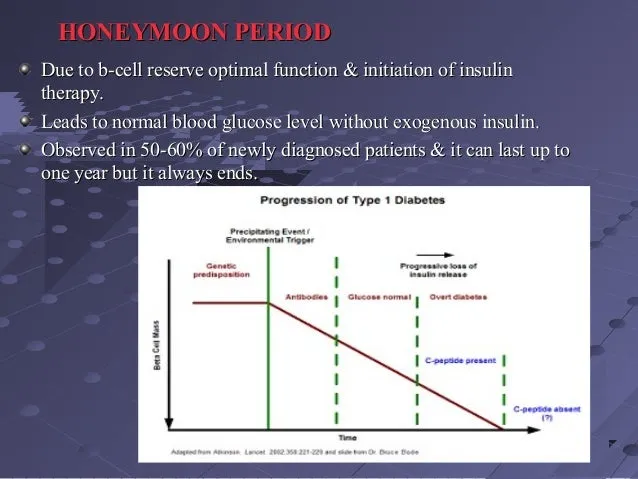
The honeymoon phase is not permanent; it will eventually end. Recognizing the signs that the honeymoon phase is coming to a close is important. These signs include rising blood sugar levels, increased insulin requirements, and the return of diabetes symptoms such as increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Be prepared to adjust your treatment plan as needed when these changes occur. Your healthcare team will help you manage the transition by adjusting your insulin dosage or making other changes to your treatment plan. Early recognition can prevent complications and help maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Managing Diabetes During the Honeymoon Phase
Living with diabetes during the honeymoon phase requires proactive management, which ensures that you stay in the best health possible. The focus should be on the following for proper management of the condition.
Healthcare Team Collaboration
Regular communication with your healthcare team is vital throughout the honeymoon phase. This team typically includes an endocrinologist, a certified diabetes educator, a registered dietitian, and potentially other specialists. Attend all scheduled appointments and share your blood sugar readings, insulin dosages, and any changes in your symptoms. Your healthcare team will provide guidance on insulin adjustments, dietary modifications, and exercise plans. They can also help address any questions or concerns you have. Open and honest communication is key to successful diabetes management. Also, support from peers and family members is invaluable.
Emotional Support and Mental Health

The diabetes honeymoon phase can bring about a roller coaster of emotions. It’s essential to prioritize your mental health and seek emotional support. Consider joining a diabetes support group or connecting with a therapist or counselor specializing in diabetes. They can help you cope with the stress, anxiety, and uncertainty that may arise during this time. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or mindfulness, can also be beneficial. Remember, managing your mental health is just as important as managing your blood sugar levels. It is crucial for overall well-being and long-term health.
Long-Term Diabetes Management
Even after the honeymoon phase ends, effective long-term diabetes management is essential. This will help prevent complications and ensure a good quality of life. It requires a holistic approach, which involves monitoring blood sugar levels, adhering to a healthy diet, staying physically active, and taking medication as prescribed. Regular check-ups with your healthcare team, including regular eye exams, foot exams, and blood tests, are also crucial. By adopting a proactive approach to diabetes management, you can live a full and healthy life, even after the honeymoon phase has passed.
Preventing Complications
Diabetes can lead to several complications if not managed correctly. These complications can affect various parts of the body, including the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart, and blood vessels. To prevent complications, maintain tight control over your blood sugar levels. Follow your healthcare team’s recommendations regarding medication, diet, and exercise. Also, attend all scheduled check-ups and screenings. Early detection and treatment of complications are crucial to minimize their impact. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, also plays a significant role in preventing complications.
Ongoing Education and Support

Diabetes management is an ongoing learning process. Seek out ongoing education and support to stay informed about the latest advances in diabetes care. Attend educational sessions, join support groups, and consult with your healthcare team to stay current on diabetes management techniques. Consider using online resources, such as reputable websites and social media groups, to connect with other people with diabetes. Continued education and support will empower you to manage your diabetes effectively and make informed decisions about your health. Staying informed will help you adapt to the changes that may occur during and after the honeymoon phase.
In conclusion, the diabetes honeymoon phase is a unique period that follows the diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Understanding its characteristics, managing it effectively, and preparing for its eventual end are critical for successful diabetes management. By working closely with your healthcare team, monitoring your blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking emotional support, you can navigate the honeymoon phase and build a solid foundation for long-term health. Remember that diabetes management is a continuous journey, and with the right approach, you can lead a fulfilling life.
